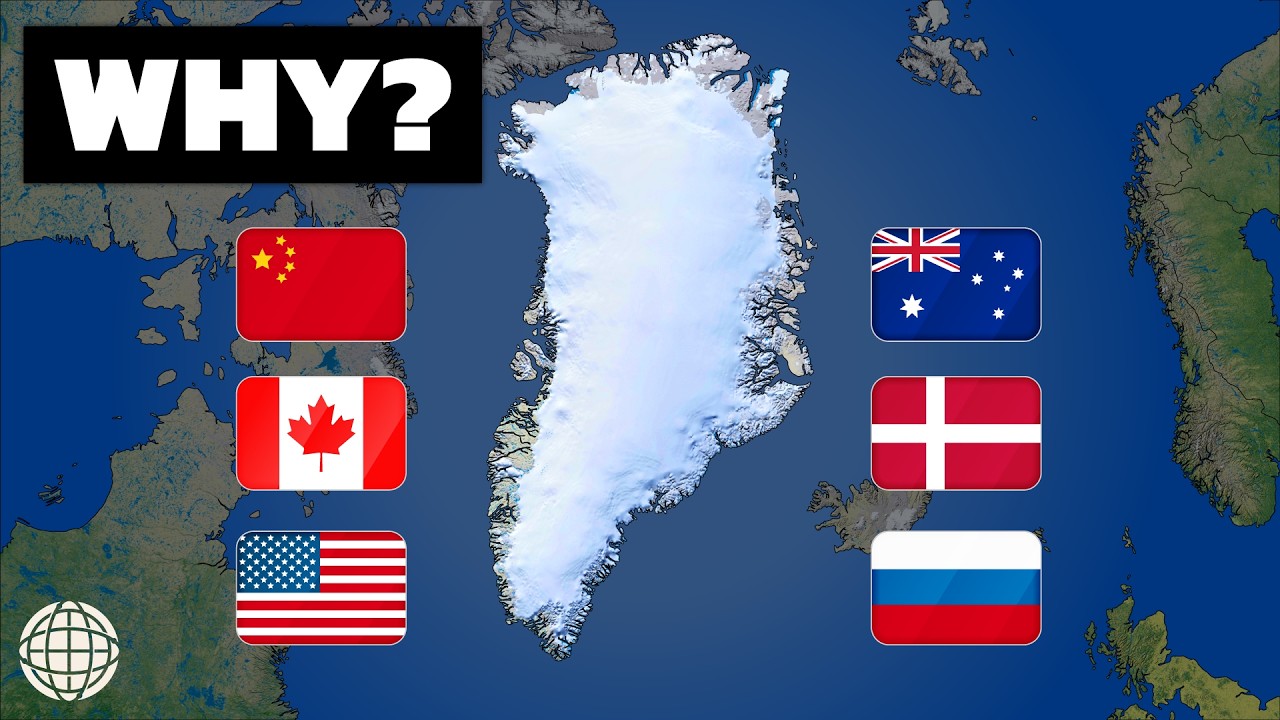
Discover why Greenland’s strategic location and resources make it crucial to global geopolitics, climate change, and sustainable development today.
Greenland, the world’s largest island, has long been a place of intrigue and fascination. Its vast landscapes, icy terrain, and rich cultural history make it a unique part of the globe. However, in recent years, Greenland has taken on an increasingly significant role on the global stage, particularly in the context of climate change, geopolitics, and natural resources. This blog post explores the multifaceted importance of Greenland today and why the world should pay attention to this remote yet critical region.
1. Climate Change and Environmental Monitoring
One of the most pressing reasons Greenland is crucial to the world today is its role in climate change. The island is experiencing some of the most rapid warming on the planet, with temperatures rising at twice the global average. This phenomenon has profound implications for sea-level rise, global weather patterns, and biodiversity.
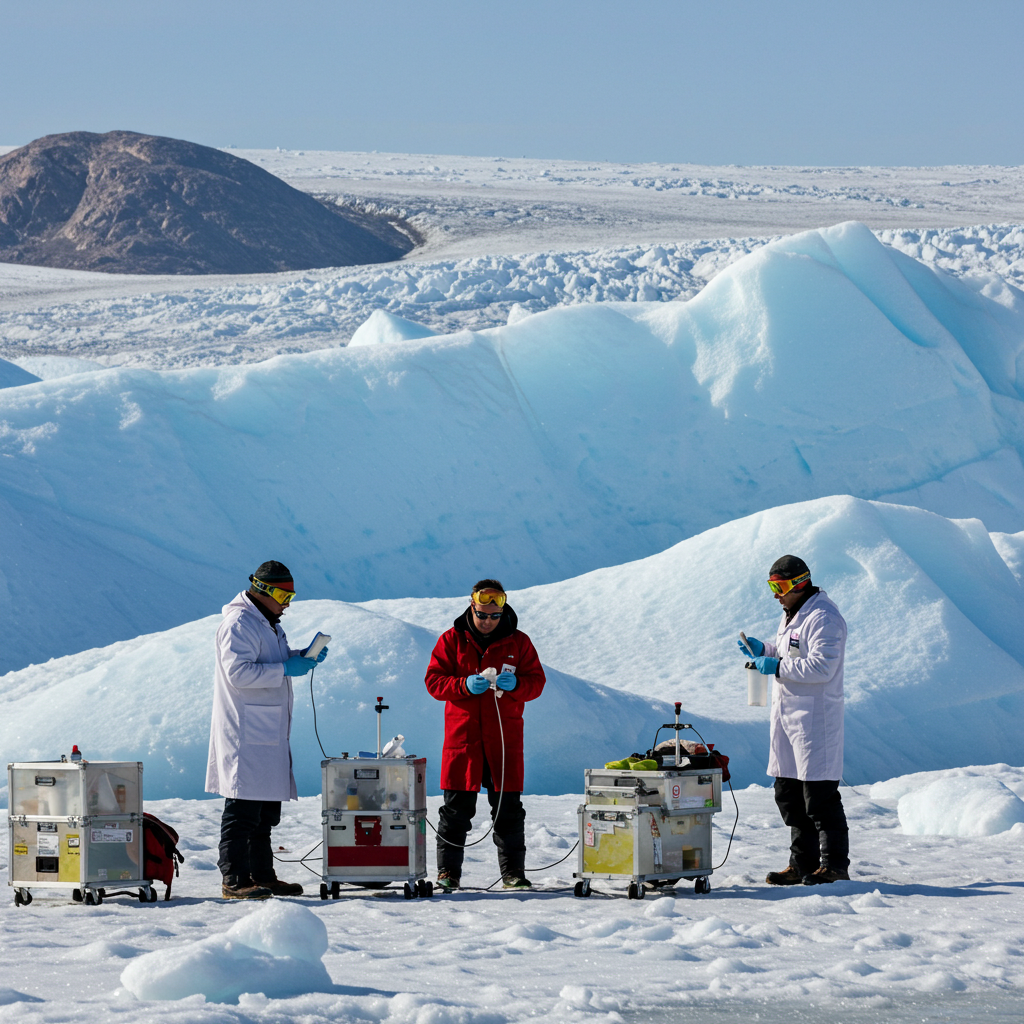

Melting Ice Sheets
Greenland’s ice sheet contains enough freshwater to raise global sea levels by over seven meters if it were to melt entirely. In recent years, scientists have observed alarming rates of ice loss, primarily due to increased surface melting and the calving of icebergs. The Greenland Ice Sheet has lost approximately 3.8 trillion tons of ice since the early 1990s, contributing significantly to rising sea levels. This melting not only threatens coastal communities around the world but also disrupts marine ecosystems and alters ocean circulation patterns.
Global Climate Indicators
Greenland serves as a crucial indicator of global climate health. Researchers study its ice cores, which provide valuable data about past climate conditions and help predict future trends. By understanding how Greenland’s environment responds to warming, scientists can better assess the potential impacts of climate change worldwide. The island’s glaciers and ice caps are also essential for understanding the dynamics of ice flow and the mechanisms driving ice loss, making Greenland a vital laboratory for climate science.
2. Geopolitical Significance
As the Arctic region becomes more accessible due to melting ice, Greenland’s geopolitical importance is growing. The Arctic is rich in natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals, and several countries are vying for control over these valuable assets.
Strategic Location
Greenland’s geographical position makes it a strategic asset for global powers. Located between North America and Europe, it serves as a critical waypoint for military and commercial shipping routes. The Northern Sea Route, which runs along the coast of Russia, is becoming increasingly navigable, and Greenland’s ports could play a vital role in facilitating trade between Europe and Asia.
Global Powers’ Interests
The United States, China, and Russia have all expressed interest in Greenland, leading to heightened tensions and competition in the region. The U.S. has long maintained a military presence in Greenland, particularly at Thule Air Base, which is crucial for monitoring missile launches and conducting satellite operations. In recent years, China has sought to increase its influence in the Arctic through investments in infrastructure and research, raising concerns in Washington and other Western capitals.
Autonomy and Self-Determination
Greenland is an autonomous territory of Denmark, and its residents are increasingly advocating for greater self-determination. The island’s government is pushing for more control over its resources and decision-making processes, reflecting a broader trend in indigenous and local governance. As Greenland seeks to assert its identity and autonomy, its geopolitical significance will likely continue to grow, making it a focal point for international relations.
3. Natural Resources and Economic Potential
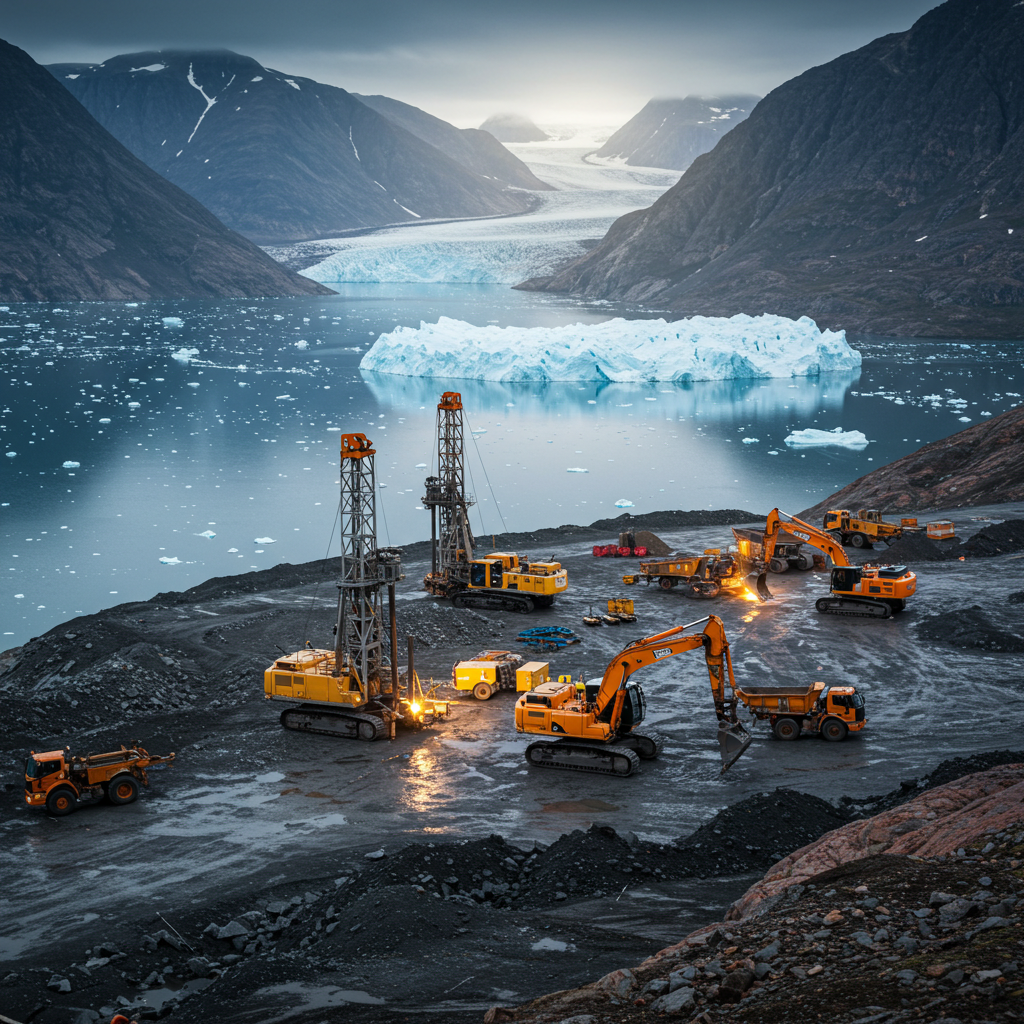
Greenland is rich in natural resources, including rare earth elements, minerals, and hydrocarbons. As global demand for these materials increases, the island’s potential as a resource hub is becoming more apparent.
Mineral Wealth
Greenland is believed to have significant deposits of valuable minerals, including gold, zinc, iron ore, and rare earth elements. These materials are essential for various industries, including technology, renewable energy, and defense. The extraction of these resources could provide a substantial economic boost to Greenland, which has historically relied on fishing and subsidies from Denmark.
Oil and Gas Exploration
The Arctic region is estimated to hold around 13% of the world’s undiscovered oil reserves and 30% of its natural gas reserves. Greenland’s offshore areas are believed to contain significant hydrocarbon resources, making them attractive for exploration and extraction. However, the environmental risks associated with drilling in such a fragile ecosystem are substantial, leading to debates about the balance between economic development and environmental protection.
Sustainable Development
As Greenland explores its resource potential, there is a growing emphasis on sustainable development. The island’s government is committed to ensuring that any resource extraction is done responsibly and benefits local communities. This approach aligns with global efforts to transition towards more sustainable practices and reduce the environmental impact of resource extraction.
4. Cultural Heritage and Indigenous Rights

Greenland is home to a rich cultural heritage and a diverse indigenous population. The Inuit people have lived on the island for thousands of years, and their traditions, knowledge, and connection to the land are vital components of Greenland’s identity.
Preserving Indigenous Culture
As globalization and climate change threaten traditional ways of life, there is an urgent need to preserve and promote Inuit culture. The Greenlandic government is actively working to support indigenous rights and ensure that the voices of local communities are heard in decision-making processes. This includes recognizing the importance of traditional ecological knowledge in managing natural resources and addressing environmental challenges.
Tourism and Cultural Exchange
In recent years, tourism has become an increasingly important sector for Greenland’s economy. Visitors are drawn to the island’s stunning landscapes, unique wildlife, and rich cultural heritage. Sustainable tourism initiatives can provide economic opportunities for local communities while promoting cultural exchange and awareness of Greenland’s challenges.
5. Scientific Research and Collaboration

Greenland is a hub for scientific research, attracting researchers from around the world who seek to study its unique environment and climate. The island offers a natural laboratory for a wide range of scientific disciplines, including glaciology, ecology, and geology.
International Research Initiatives
Collaboration among international research institutions is crucial for understanding the complexities of Greenland’s environment. Programs like the Greenland Ecosystem Monitoring (GEM) project and the Arctic Research Initiative bring together scientists from various countries to study the impacts of climate change, biodiversity, and ecosystem dynamics. These collaborative efforts enhance our understanding of the Arctic and its global significance.
Education and Capacity Building
Investing in education and capacity building in Greenland is essential for fostering a new generation of scientists and researchers. Local universities and institutions are increasingly focusing on Arctic studies, providing opportunities for Greenlandic students to engage in research and contribute to the global scientific community. By empowering local talent, Greenland can enhance its role in scientific research and innovation.
Conclusion
Greenland is at the center of some of the most pressing issues facing the world today, from climate change and geopolitical tensions to resource management and cultural preservation. Its melting ice sheets serve as a stark reminder of the urgent need for global action on climate change, while its rich natural resources present both opportunities and challenges for sustainable development.
As the world continues to grapple with these complex issues, it is crucial to recognize and respect the voices of Greenland’s indigenous communities and support their rights to self-determination. By fostering international collaboration and sustainable practices, we can work together to ensure that Greenland’s unique environment and culture are preserved for future generations.
In a rapidly changing world, Greenland stands as a symbol of both the challenges we face and the opportunities that lie ahead. Its importance to the global community cannot be overstated, and as we move forward, we must prioritize the protection of this remarkable island and its people.

