Explore the escalating trade war between China and the U.S. Discover strategies, impacts, and the lengths China may go to secure its economic dominance.
Introduction
The trade war between China and the United States has become one of the most significant economic conflicts of the 21st century. It began in earnest in 2018 when the U.S. imposed tariffs on Chinese goods, citing unfair trade practices and intellectual property theft. In response, China retaliated with its own tariffs, leading to a tit-for-tat escalation that has had far-reaching implications for both economies and the global market. This blog explores the motivations behind China’s actions, the strategies it may employ to counter U.S. influence, and the potential consequences of this ongoing conflict.

The Roots of the Trade War
Economic Competition
At its core, the trade war is about economic competition. The U.S. has long held the position of the world’s largest economy, but China’s rapid growth over the past few decades has challenged that status. China’s ascent has been fueled by a combination of state-led capitalism, a massive labor force, and significant investments in technology. As China continues to grow, the U.S. perceives it as a threat to its economic dominance.
Intellectual Property Theft
One of the primary grievances of the U.S. is the alleged theft of intellectual property by Chinese companies. American businesses have accused China of requiring foreign firms to transfer technology as a condition for market access. This practice not only undermines U.S. innovation but also provides China with the tools to compete on a global scale. The U.S. government argues that protecting intellectual property is essential for maintaining its competitive edge.
Trade Imbalances
Another factor contributing to the trade war is the significant trade imbalance between the two nations. The U.S. has consistently run a trade deficit with China, importing far more than it exports. This imbalance has fueled political rhetoric about the need to “level the playing field” and has led to calls for tariffs and other trade barriers.
China’s Response to U.S. Actions
Retaliatory Tariffs
In response to U.S. tariffs, China implemented its own tariffs on American goods, targeting industries such as agriculture, automotive, and technology. These retaliatory measures were designed to put pressure on U.S. producers and create domestic discontent. For example, tariffs on U.S. soybeans and pork were aimed at hurting American farmers, many of whom are crucial supporters of the Republican Party.
Strengthening Domestic Industries
China has also sought to reduce its reliance on U.S. technology and goods by investing heavily in domestic industries. The “Made in China 2025” initiative aims to make China a global leader in high-tech sectors such as robotics, artificial intelligence, and renewable energy. By fostering homegrown innovation, China hopes to diminish the impact of U.S. tariffs and create a more self-sufficient economy.
Diplomatic Maneuvering
China’s response has not been limited to economic measures. The country has engaged in diplomatic efforts to strengthen ties with other nations and create alternative markets for its goods. By enhancing relationships with countries in Africa, Southeast Asia, and Europe, China aims to mitigate the effects of U.S. tariffs and maintain its economic growth.
The Future of the Trade War
Escalation of Tensions
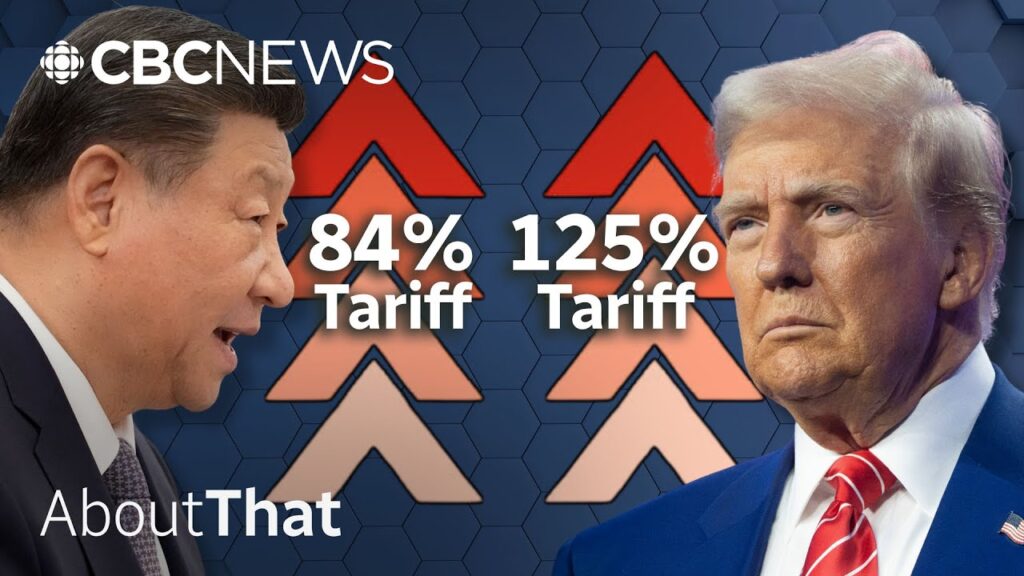
As the trade war continues, the potential for escalation remains high. Both nations have demonstrated a willingness to engage in aggressive tactics, including sanctions and trade barriers. The U.S. has threatened to impose additional tariffs, while China may respond with more retaliatory measures. This cycle of escalation could lead to a prolonged conflict that disrupts global trade and economic stability.
Impact on Global Supply Chains
The trade war has already begun to affect global supply chains. Many companies are reevaluating their operations and considering relocating production to avoid tariffs. This shift could have significant implications for countries that rely on manufacturing and export-oriented industries. As businesses adapt to the changing landscape, the interconnectedness of the global economy will be tested.
Long-Term Economic Consequences
The long-term economic consequences of the trade war are difficult to predict. While some sectors may benefit from increased protectionism, others will likely suffer. For instance, American consumers may face higher prices for goods due to tariffs, while Chinese manufacturers may struggle to find alternative markets for their products. The overall impact on global economic growth could be negative, leading to slower progress for both nations.
China’s Strategic Goals
Achieving Technological Independence
One of China’s primary goals in the trade war is to achieve technological independence. By investing in research and development, China aims to reduce its dependence on foreign technology and become a leader in innovation. This ambition is evident in initiatives like “Made in China 2025,” which seeks to advance key industries and foster homegrown talent.
Expanding Global Influence
China is also focused on expanding its global influence. By engaging in trade partnerships and investments in infrastructure projects, such as the Belt and Road Initiative, China aims to solidify its position as a global economic powerhouse. This strategy not only enhances China’s economic standing but also allows it to counter U.S. influence in various regions.
Maintaining Domestic Stability
Another critical goal for China is maintaining domestic stability. The Chinese government understands that economic growth is essential for social stability. By mitigating the effects of the trade war and ensuring continued economic progress, the government hopes to maintain public support and prevent unrest.
The Role of International Alliances
Strengthening Ties with Other Nations
China has sought to strengthen ties with other nations as a counterbalance to U.S. influence. By forming strategic partnerships and engaging in trade agreements, China aims to create a network of allies that can support its economic ambitions. This approach not only helps China secure new markets but also undermines U.S. efforts to isolate it diplomatically.
Engaging in Multilateral Institutions
China is increasingly active in multilateral institutions, such as the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC). By participating in these organizations, China can advocate for its interests and promote a narrative that counters U.S. claims. This engagement allows China to position itself as a champion of free trade and economic cooperation.
Conclusion
The trade war between China and the United States is a complex and evolving conflict that poses significant challenges for both nations and the global economy. As China continues to assert its influence and pursue its strategic goals, the question remains: how far will China go to beat the U.S.? The answer will depend on a myriad of factors, including economic conditions, domestic stability, and international alliances. Ultimately, the outcome of this trade war will shape the future of global trade and the balance of power in the international arena..
In navigating this uncertain landscape, both countries must consider the broader implications of their actions. A prolonged trade war could lead to economic stagnation, disrupted supply chains, and increased tensions. Finding a path toward cooperation and dialogue may be the key to mitigating the risks associated with this ongoing conflict. As the world watches closely, the stakes have never been higher, and the future remains uncertain.

